Engine Diagnostics

BMW Engine Diagnostics: Common Issues, Codes, and Troubleshooting Guide
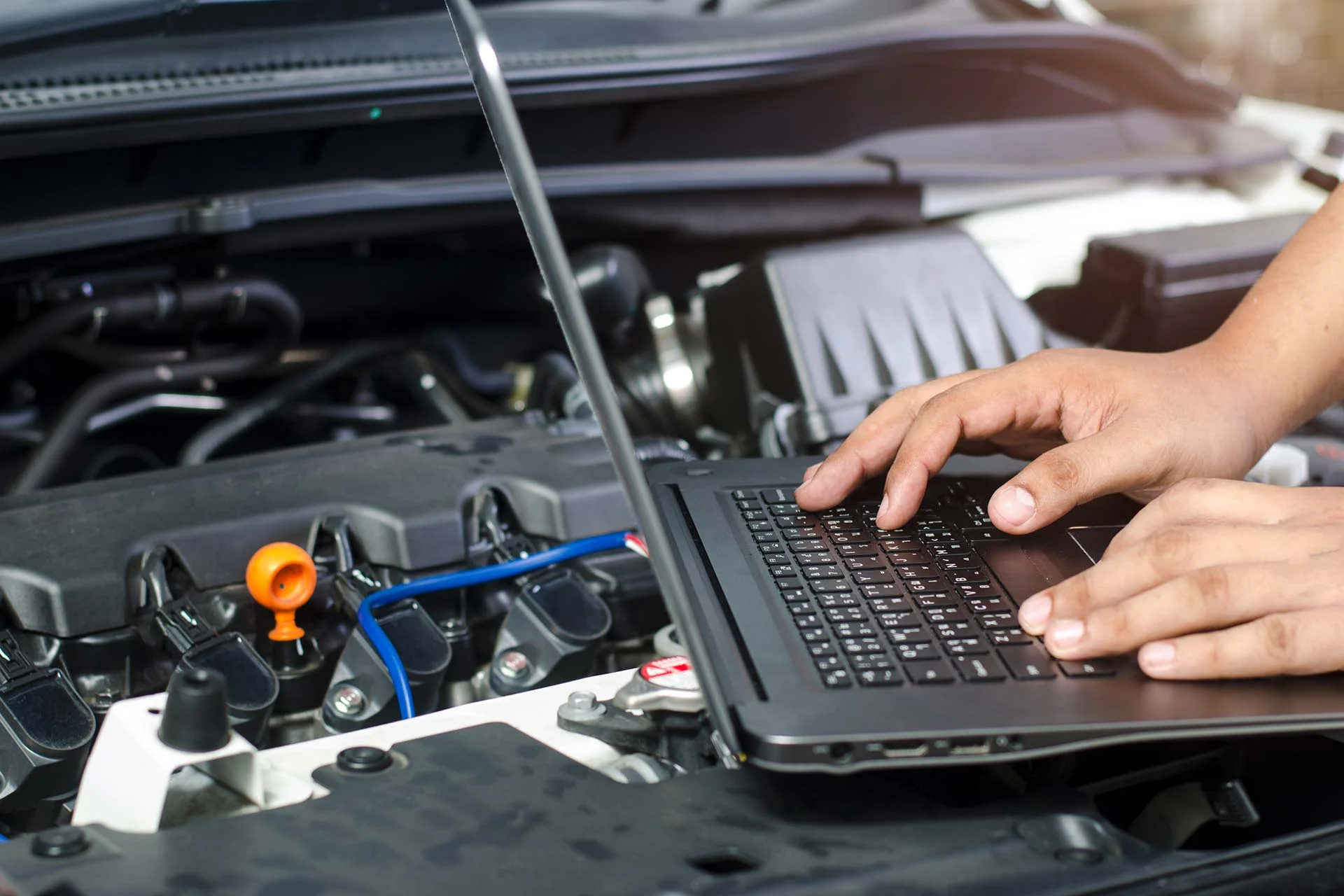
Engine diagnostics can help identify a wide range of issues affecting performance, fuel efficiency, and reliability. Recognizing the symptoms and associated trouble codes allows for more accurate and timely repairs.

Fuel System Issues
Fuel Injector Malfunction
- Symptoms: Misfires, poor fuel economy, rough idle.
- Trouble Codes: P0301-P0306 (Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0172 (System Too Rich), P0171 (System Too Lean).
High-Pressure Fuel Pump (HPFP) Failure
- Symptoms: Long crank times, reduced power, and loss of boost on turbocharged models.
- Trouble Codes: 2FBA (Fuel Pressure Too Low), 2FBF (Fuel Pressure After Shutoff).
Scan for Misfire Codes
Check for specific cylinder misfire codes to pinpoint failing injectors.
Monitor Fuel Pressure
Use a scan tool to observe fuel rail pressure. Consistently low pressure suggests an HPFP issue.
Inspect Fuel Injectors
Test for leaks or fuel buildup around injectors, and replace any faulty units.
Check Fuel Trim
A lean or rich condition in the fuel trim can indicate injector or fuel pump problems.
Ignition System Issues
Faulty Spark Plugs or Ignition Coils
- Symptoms: Misfires, rough idle, engine hesitation.
- Trouble Codes: P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0350-P0356 (Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction).

Weak Battery or Faulty Alternator
- Symptoms: Difficulty starting, electrical malfunctions, misfire under load.
- Trouble Codes: P0562 (System Voltage Low), P0620 (Generator Control Circuit Malfunction).
Inspect Spark Plugs
Check for fouling or wear; replace if needed.
Test Ignition Coils
Swap coils between cylinders to see if the misfire follows, indicating a faulty coil.
Monitor Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can affect ignition performance; test battery and alternator output.
Replace as Needed
Replace worn or fouled spark plugs and faulty coils to restore ignition performance.
Intake System Issues

Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Malfunction
- Symptoms: Rough idle, stalling, poor fuel economy.
- Trouble Codes: P0101 (MAF Circuit Range/Performance Problem), P0102 (MAF Circuit Low Input).

Vacuum Leaks
- Symptoms: Rough idle, hissing sound, lean fuel condition.
- Trouble Codes: P0171 (System Too Lean Bank 1), P0174 (System Too Lean Bank 2).
Inspect MAF Sensor
Clean the MAF sensor if it’s dirty; replace it if it continues to throw codes.
Check for Vacuum Leaks
Use smoke testing or carb cleaner around intake areas to identify leaks.
Monitor Short-Term Fuel Trim
Lean conditions often result from vacuum leaks or MAF issues.
Inspect Intake Boots and Hoses
Cracks in intake hoses and boots can cause unmetered air to enter, resulting in lean codes.
Exhaust and Emissions Control Issues
O2 Sensor Failure
- Symptoms: Poor fuel economy, rough idle, check engine light.
- Trouble Codes: P0130-P0135 (O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction), P0140 (O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected).
Catalytic Converter Efficiency Issues
- Symptoms: Reduced power, poor fuel economy, sulfur smell.
- Trouble Codes: P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 1), P0430 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 2).
Monitor O2 Sensor Readings
Use a scan tool to monitor O2 sensor output; failing sensors will give slow or no response.
Check Catalyst Efficiency
If catalyst codes appear, test the catalytic converter for restrictions or efficiency loss.
Inspect Exhaust for Leaks
Exhaust leaks before the O2 sensors can skew readings and cause codes.
Replace Sensors as Needed
O2 sensors wear out over time; replace them if they’re causing inefficiencies.
Cooling System Issues
Thermostat Failure
- Symptoms: Overheating, coolant leaks, engine temperature fluctuations.
- Trouble Codes: P0128 (Coolant Thermostat Below Regulating Temperature).

Water Pump Failure
- Symptoms: Overheating, reduced coolant flow, limp mode.
- Trouble Codes: 2E81 (Electric Water Pump Speed Deviation), 2E82 (Electric Water Pump Shutoff).
Scan for Cooling System Codes
Thermostat or water pump codes indicate issues with temperature regulation.
Monitor Coolant Temperature
Use a scan tool to check coolant temperatures; fluctuating temperatures suggest thermostat issues.
Check for Coolant Leaks
Inspect around the water pump, thermostat housing, and radiator for leaks.
Replace Faulty Components
Electric water pumps and thermostats are common points of failure; replace as needed.
Variable Valve Timing (VANOS) Issues

VANOS Solenoid Failure
- Symptoms: Rough idle, loss of power, delayed throttle response.
- Trouble Codes: P1520-P1525 (Variable Valve Timing Solenoid Malfunction), 2A82 (Intake VANOS Mechanism), 2A87 (Exhaust VANOS Mechanism).
Test VANOS Solenoids
Clean or replace solenoids if codes or performance issues persist.
Monitor Oil Quality
Dirty oil can clog VANOS solenoids; regular oil changes are crucial.
Check Timing
Improper timing can throw VANOS codes; verify timing if issues persist.
Replace O-Rings
Worn VANOS o-rings can leak and reduce system effectiveness.
Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System Issues
PCV Valve Failure
- Symptoms: Oil leaks, excessive oil consumption, rough idle.
- Trouble Codes: P0507 (Idle Control System RPM Higher Than Expected), P0171 (System Too Lean).
Inspect PCV Valve
Test the PCV valve for clogs or malfunction; replace if necessary.
Look for Oil in Intake
A failing PCV valve can cause oil to collect in the intake manifold.
Monitor Fuel Trim
Lean conditions and high idle can point to PCV system issues.
Check for Excessive Crankcase Pressure
This can cause oil leaks around the valve cover and other seals.
Engine Mechanical Issues
Timing Chain Wear or Stretch
- Symptoms: Rattling noise from the engine, poor performance, potential engine damage.
- Trouble Codes: P0016 (Crankshaft Position – Camshaft Position Correlation), P0017 (Camshaft Position Correlation Bank 1 Sensor B).
Low Compression in Cylinders
- Symptoms: Misfires, poor acceleration, rough idle.
- Trouble Codes: Often results in multiple misfire codes, such as P0300-P0306.
Inspect Timing Components
If timing-related codes appear, inspect the chain and tensioner for wear.
Perform a Compression Test
Check each cylinder’s compression to identify weak or failed cylinders.
Replace Timing Components as Needed
Timing chain stretch is a serious issue requiring prompt attention.
Listen for Rattling Sounds
Rattling from the front of the engine may indicate timing chain tensioner wear.